Iceland Supermarkets to Ban Palm Oil in Own-Brand Products

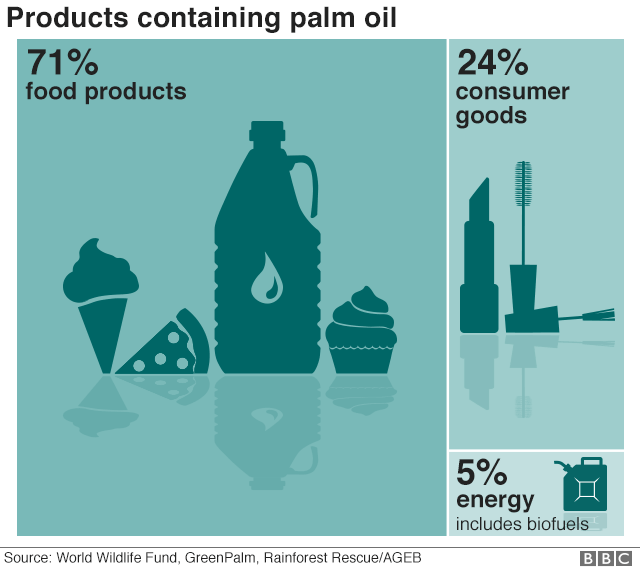
Unfortunately, palm oil is still used widely as a filler in many packaged and processed foods, as well as a crude oil to burn and create biofuel. The EU has decided to limit the use of palm oil in biofuels, hopefully cutting back on the environmental impact, but Malaysia has had growing concerns about being cut-off from trade.
UPcycling to the Market: Reducing Food Waste and Building a New Economy
Check out this article about several start-up companies upcycling surplus or partially used resources/materials such as coffee been husks for another kind of coffee/tea brew (like Cascara) or beer even. The article addresses how upcycling a surplus ingredient might make sense, but sometimes not. Such is the case when creating a product from the upcycled material requires more work or more materials.
You Are WHAT You EAT: What’s in Your Food?
Studies Continue to Link to Carrageenan to Inflammation, Cancer, and Diabetes

NOSB was overruled by Trump’s Administration to keep carrageenan out of our organic foods. BOO.
“After eight years of Cornucopia’s research, advocacy, and petitioning, the National Organic Standards Board (NOSB) voted in November 2016 to remove carrageenan, a potent inflammatory agent and possible carcinogen, from the National List for use in organics.” The food additive which can be found in everything from ice cream to a variety of processed, even certified organic, foods is reported by scientists to contribute to “gastrointestinal inflammation, including higher rates of colon cancer, in laboratory animals.” Read the full article by the Cornucopia Institute online here.
Food Labeling Isn’t Easy, But Let’s Keep the Pressure On
“While many brands and scientists contend that carrageenan is a safe food additive, the NOSB, which advises the National Organic Program, eventually voted to revoke its recommendation of the ingredient from the approved list in 2016.” – Organic Authority
“The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) is excepted to release its long-awaited bio-engineered (GMO) disclosure label rules in the next several days or weeks, which will establish a national standard for labeling foods containing GMO ingredients. Meanwhile, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) confirmed that it is pressing ahead with many label issues and initiatives, such as conducting a review to modernize standards of identity, ingredient statement requirements, and food label claims, such as creating a definition for the term “healthy” with a corresponding label symbol. Further, Congress has stepped into the conversation. Recently, the House of Representatives passed a bill called the Common Sense Nutrition Disclosure Act to weaken menu label requirements for restaurants and retailers, as was mandated by the Affordable Care Act.“
Read more here on the National Review for the full article and more information about various laws and legislation, and matters relating to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and US Department of Agriculture (USDA).
U.S. Farmers Likely To Be Among Hardest Hit By Chinese Tariffs by NPR
Follow the story on NPR about the most recent changes to trade agreements between the United States and China, and exactly who will be affected by increased costs to corn, soybeans, wheat, cotton and beef. “China has become the largest customer for America’s farm products, buying well over $20 billion per year. China bought more than $1 billion in U.S. pork last year. But this week, it threatened a 25 percent tariff on that pork and 15 percent tariffs on a host of farm products grown across a wide swath of the country, including nuts.” – NPR, the Salt

Comments are closed.